
Verb Tenses in English
English verb tenses are essential to learning because they form the foundation of the English language and are used to express various meanings and ideas. They also help to explain the subject-verb relationship and to show the time, duration, frequency, and other aspects of an action or state. Verb Tenses in English are verb forms that express time.
By studying English verb tenses, students can become more fluent and better able to communicate in English. Additionally, a strong understanding of verb tenses will help students avoid errors in their writing.
A tense, in grammar, is a category that expresses time reference related to the moment of speaking.
There are 3 main tenses:
- Past
- Present
- Future
Tenses are subdivided in:
- Simple
- Continuous
- Perfect
- Perfect Continuous
Table with all Verb Tenses
| VERB TENSE | Present | Past | Future |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple | go(es) | went | will go (going to go) |
| Continuous or Progressive | am/is/are going | was/were going | will be going |
| Perfect | have/has gone | had gone | will have gone |
| Perfect Continuous or Perfect Progressive | have/has been going | had been going | will have been going |
Past
In English, the past tense refers to a completed action in the past. It is formed by appending -ed or -d to a verb’s base form or by using the irregular form of the verb. The past tense can be used to describe a specific point in time or an entire period of time that has already passed. The past tense can also be used to describe a past habit or state that no longer exists.
PAST is used to tell you when something happened (yesterday).
The PAST TENSE is subdivided into 4 Tenses, CLICK the one you would like to study more:
Past Tense – Examples
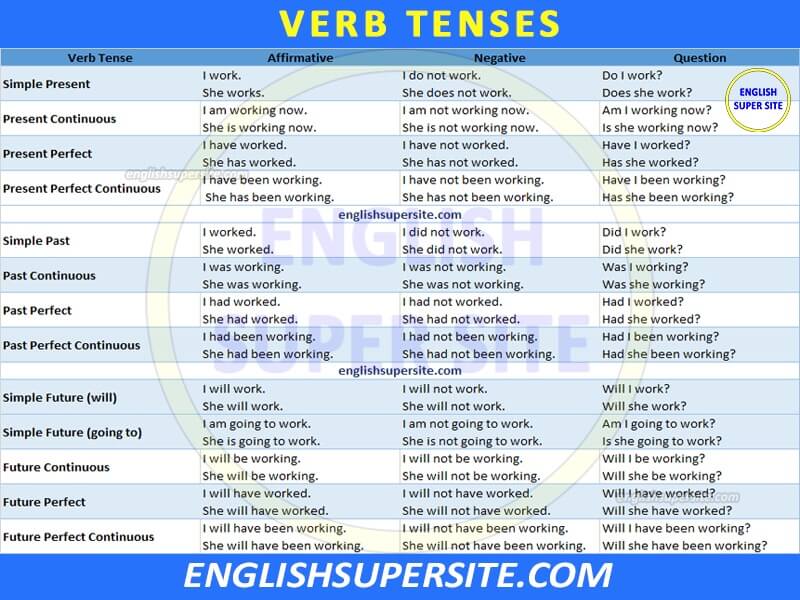
| Verb Tense | Affirmative | Negative | Question |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Past | I worked. She worked. | I did not work. She did not work. | Did I work? Did she work? |
| Past Continuous | I was working. She was working. | I was not working. She was not working. | Was I working. Was she working? |
| Past Perfect | I had worked. She had worked. | I had not worked. She had not worked. | Had I worked? Had she worked? |
| Past Perfect Continuous | I had been working. She had been working. | I had not been working. She had not been working. | Had I been working? Had she been working? |
Present
In English, the present tense is used to describe actions that are currently taking place or that occur on a regular basis. It is also used to describe states that are true right now. For the third person singular (he, she, it), add -s or -es to the end of the verb, and for all other persons, use the base form of the verb (I, you, we, they).
PRESENT is used to describe things that are happening right now (today).
The PRESENT TENSE is subdivided into 4 Tenses, CLICK the one you would like to study more:
Present Tense – Examples
| Verb Tense | Affirmative | Negative | Question |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Present | I work. She works. | I do not work. She does not Work. | Do I work? Does she work? |
| Present Continuous | I am working now. She is working now. | I am not working now. She is not working now. | Am I working now? Is she working now? |
| Present Perfect | I have worked. She has worked. | I have not worked. She has not worked. | Have I worked? Has she worked? |
| Present Perfect Continuous | I have been working. She has been working. | I have not been working. She has not been working. | Have I been working? Has she been working? |
Future
The future tense is used to describe events that will occur in the future. It is formed by combining the auxiliary verb “will” with the verb’s base form. “I’ll go to the store tomorrow,” for example. Or using the form “going to”, for example, “I am going to the mall, do you want to come with me?”
FUTURE is used to tell you that things have yet to happen (tomorrow).
The FUTURE TENSE is subdivided into 4 Tenses, CLICK the one you would like to study more:
Future Tense – Examples
| Verb Tense | Affirmative | Negative | Question |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Future (will) | I will work. She will work. | I will not work. She will not work. | Will I work? Will she work? |
| Simple Future (going to) | I am going to work. She is going to work. | I am not going to work. She is not going to work. | Am I going to work? Is she going to work? |
| Future Continuous | I will be working. She will be working. | I will not be working. She will not be working. | Will I be working? Will she be worknig? |
| Future Perfect | I will have worked. She will have worked. | I will not have worked. She will not have worked. | Will I have worked? Will she have worked? |
| Future Perfect Continuous | I will have been working. She will have been working. | I will not have been working. She will not have been working. | Will I have been working? Will she have been working? |
Verb Tenses – Examples – Image
Conditional – Future-in-the-past
CONDITIONAL is used in the main clause accompanied by an implicit or explicit condition (if-clause). The time referred to may be (hypothetical) present or future.
Verb tenses explain the time range in which an action occurs. The conditional form of verb tenses is used to indicate activities that are depending on the fulfillment of a certain condition or collection of conditions.
The CONDITIONAL TENSE is subdivided into 4 Tenses:
- Simple Conditional or Conditional Present: would go
- Conditional Continuous (Progressive): would be going
- Conditional Perfect: would have gone
- Conditional Perfect Continuous (Progressive): would have been going
Study Also:
Abbreviations Cohesion and Coherence Collocations Comparative Conditionals Frequent Errors Future Continuous Future Perfect Future Perfect Continuous Future Simple Homonyms Interjections Journaling Learn English Linking Words Logical Flow Past Continuous Past Perfect Past Perfect Continuous Past Simple Plural Present Continuous Present Perfect Present Perfect Continuous Present Simple Pronunciation Question Tags Quiz Quotes Simple Future Simple Past Simple Present Spelling Superlative Transition Words
Share with your friends!






























